From Player To Professional
Working on video games is a dream for many, but turning that dream into a real job requires more than passion alone. Studios look for specific abilities that support teamwork, problem-solving, and player-focused thinking. When you know what those skills are, learning becomes more purposeful and less overwhelming. Instead of guessing where to start, it helps to see the bigger picture first—so let’s begin with the core skills that matter most in game development.
1. Game Design Fundamentals
Design roles demand a deep understanding of what keeps players engaged versus frustrated. The best designers craft mechanics that feel rewarding from the first moment. Level designers use these same principles when building worlds that players actually want to explore repeatedly.
2. Programming (C++, C#, Python)
Game engines depend on C++ and C#, while Python handles automation and tool development. Technical positions require strong coding abilities in at least one major language. Studios constantly search for programmers who can implement reliable systems and solve complex bugs under tight deadlines.
3. 3D Modeling
Every visual element starts as polygons shaped in Maya or Blender. Artists create characters, props, and entire environments that players interact with throughout the game. Performance optimization matters just as much as visual quality. Environment artist and character modeler positions need this foundation.
4. Animation
Movement brings virtual worlds to life through careful attention to timing and weight. Characters need to walk convincingly and express emotions through subtle body language. Strong observation skills help animators capture natural motion accurately.
 Ion (Ivan) Sipilov on Unsplash
Ion (Ivan) Sipilov on Unsplash
5. Concept Art
Early sketches establish the visual direction before any 3D work begins. These drawings define mood, color schemes, and the overall aesthetic that guides the entire team. Art directors depend on concept artists to maintain consistency throughout development.
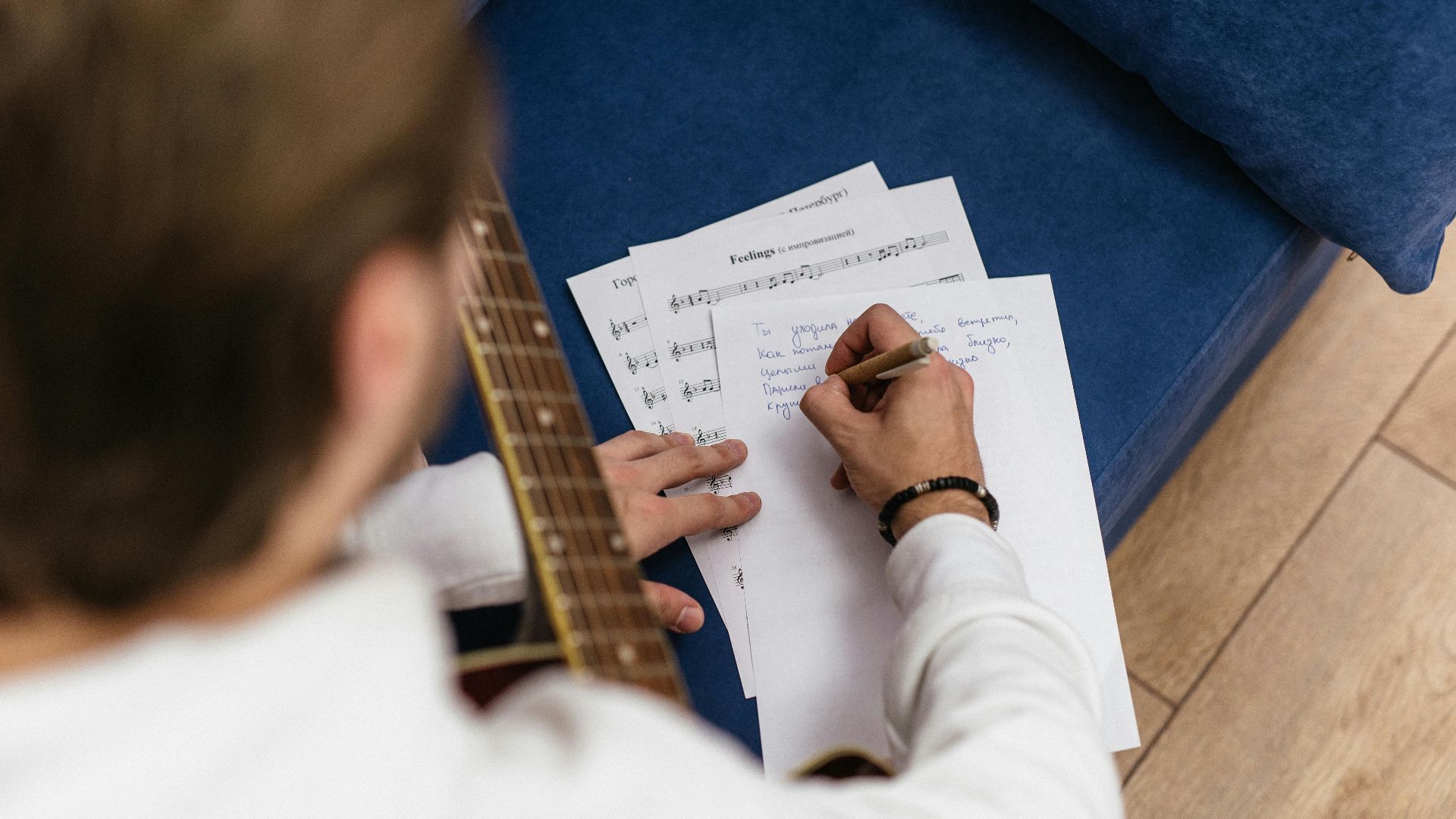
6. Storytelling & Narrative Design
Many games need compelling plots and meaningful dialogue that resonates with players. Branching narratives require careful planning, so choices feel consequential rather than superficial. Writers collaborate closely with designers to weave story elements into gameplay naturally. RPGs and adventure games particularly value strong narrative skills.
7. Sound Design
Atmosphere comes alive through carefully crafted audio that supports every player action. Weapon effects, environmental ambience, and UI feedback all need precise attention. Believable virtual worlds depend on sounds matching what's happening visually. Studios across all platforms seek audio engineers who understand immersion through sonic detail.
8. Cybersecurity For Games
Online systems face constant threats from hackers attempting to exploit vulnerabilities. Player data needs protection, while competitive integrity must be maintained against cheaters. Multiplayer experiences collapse when security fails, and exploits run unchecked. This role combines programming knowledge with adversarial thinking to stay ahead of potential attacks.
9. Quality Assurance (QA) Testing
QA testers spot bugs before players ever touch the game. They replay sections, log issues, and ensure stability. Many developers start in QA, where clear communication and sharp attention to detail matter more than advanced technical expertise.
10. Project Management
Teams need coordination to hit milestones while staying within budget constraints. Producers balance creative ambitions against practical realities like time and resources. They resolve conflicts and keep everyone moving toward shared goals. Both organizational abilities and understanding of game development processes are essential for this role.
11. User Interface (UI) Design
Menus and HUDs should guide players without overwhelming them. Effective UI uses hierarchy to highlight what matters most. When navigation feels effortless, the interface disappears. Designers combine technical tools with player psychology to create smooth, intuitive experiences.
12. User Experience (UX) Research
Player feedback is vital for spotting problems missed during development. Testing highlights pain points and moments of lost interest. UX researchers study patterns and suggest improvements, so games remain inclusive and enjoyable for diverse audiences.
13. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Development
NPC behavior needs to challenge players appropriately without feeling unfair or predictable. Pathfinding, decision trees, and adaptive systems all require careful programming. Strategy games and RPGs especially depend on enemies that respond intelligently. This specialization blends technical programming with design thinking about player experience.
14. Physics Simulation
Realistic physics keeps gameplay convincing. Racing titles demand precise handling, while action games depend on solid collision responses. Behind the scenes, math and physics drive these systems. When objects move unnaturally, players notice immediately, so accurate simulation is critical.
15. Multiplayer Networking
Smooth online play depends on multiplayer networking. Server design and latency management become harder as player counts rise. Engineers must blend programming skills with distributed systems knowledge to ensure competitive games run reliably and responsively.
16. Marketing & Community Management
Games need promotion and ongoing player engagement to build lasting success. Social media presence and direct communication with fans create loyal communities. Marketing teams craft authentic messages that resonate with target audiences, and community managers often become the public face representing a studio's values and personality.
17. Data Analytics
Metrics reveal how players actually behave versus what designers originally intended. Retention rates, progression bottlenecks, and spending patterns all inform future updates. Live-service games particularly depend on continuous analysis for optimization. Strong analytical abilities combined with business awareness make these insights actionable for development teams.
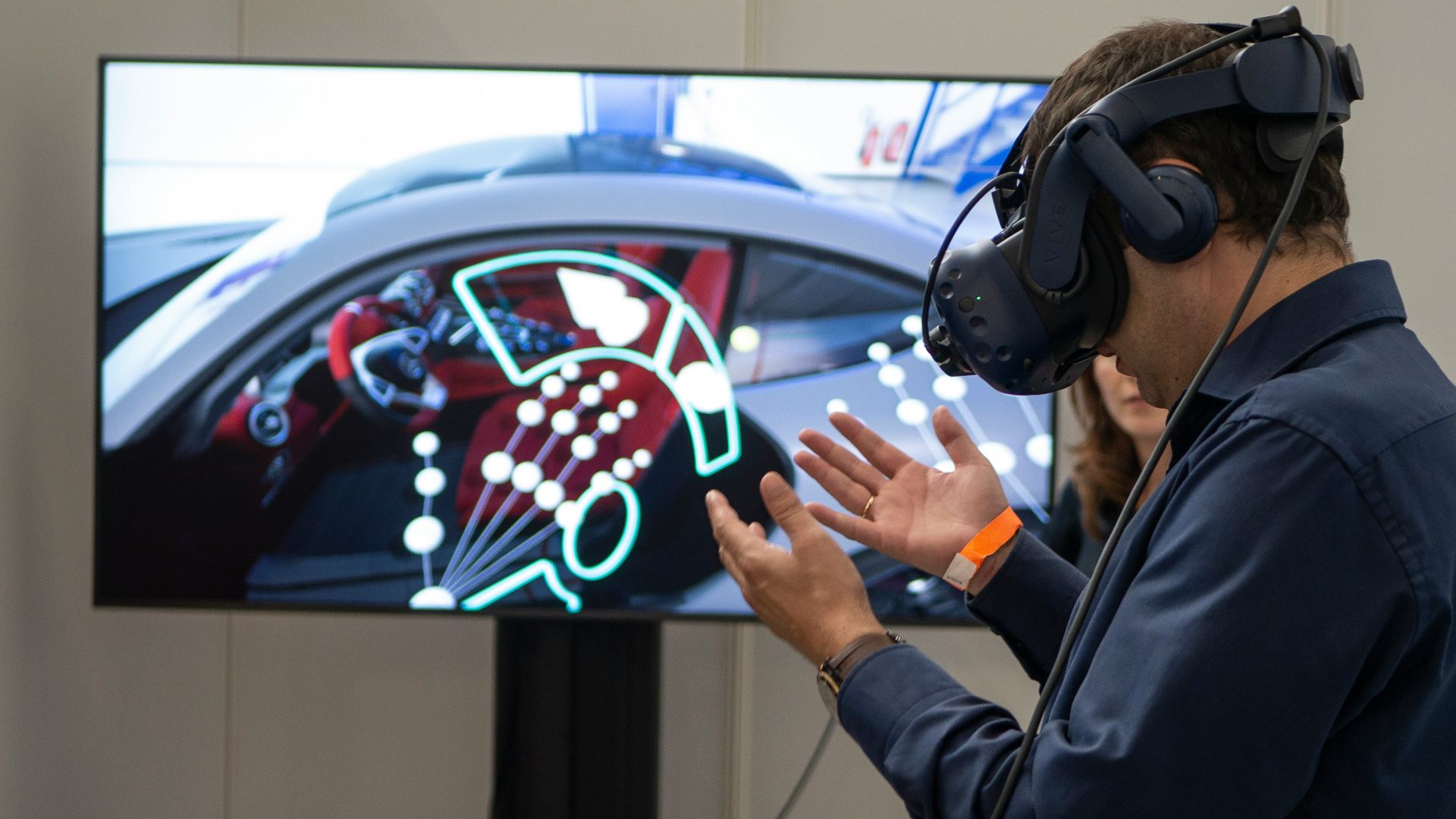
18. Virtual Reality (VR) Development
Building VR experiences requires more than immersion. Developers must prevent motion sickness and design spatial interactions. With training and specialized applications embracing VR, success depends on balancing realism with comfort to keep players engaged.
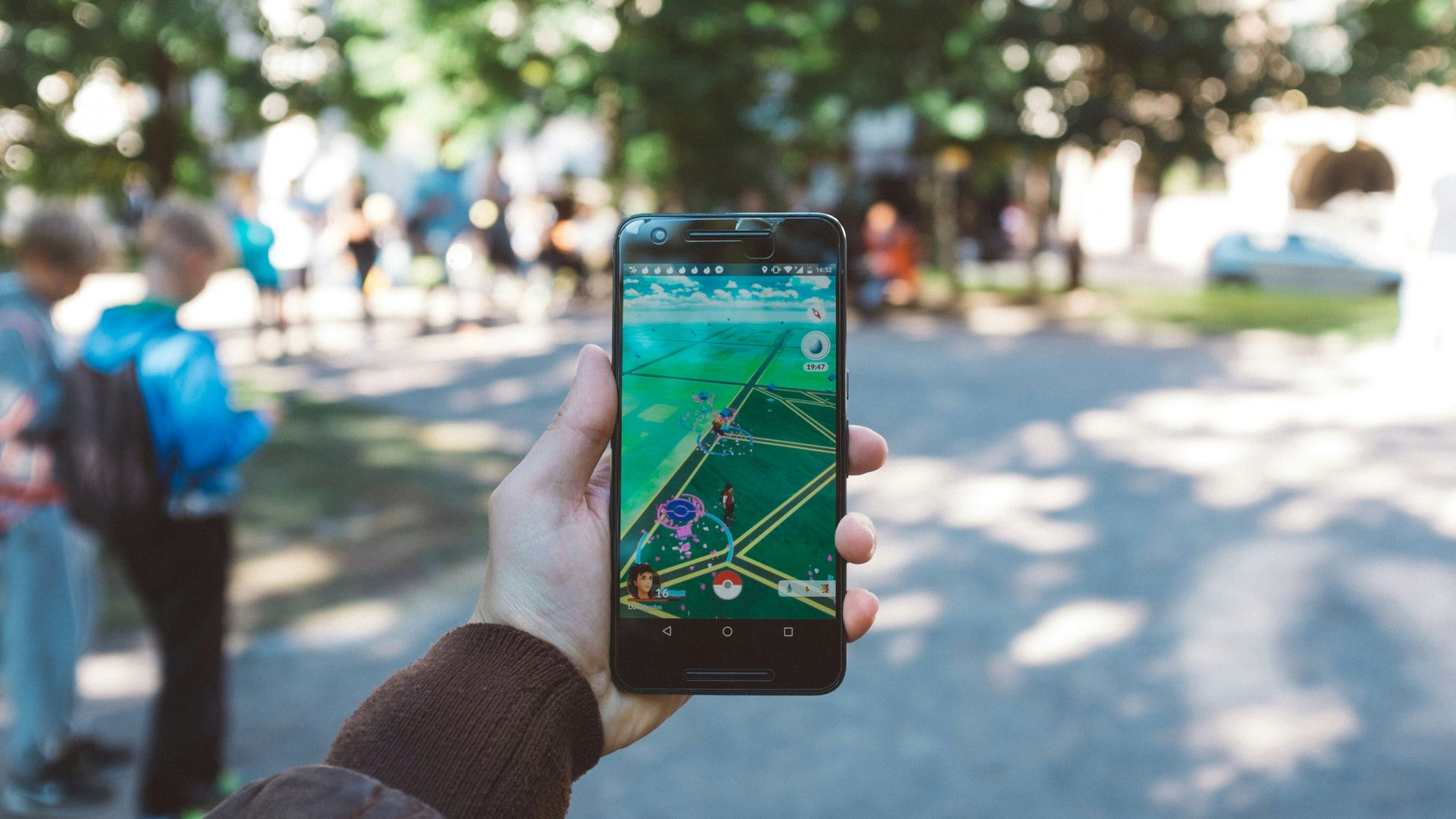
19. Augmented Reality (AR) Design
AR overlays digital elements onto the physical world. Mobile devices make these experiences widely accessible, and location‑based games prove their mass appeal. Designers must rethink spatial interaction and apply creative problem‑solving to imagine fresh uses for this emerging technology.
20. Music Composition
Game music adds emotional depth without distracting from play. Combat scores fuel excitement, exploration tracks inspire wonder, and dynamic systems adjust to player choices. Modern composers must combine strong melodies with adaptive techniques to create soundscapes that feel alive and unforgettable.