A Faster, More Connected Baseline
Over the past two decades, everyday technology has shifted so rapidly that you probably can't think about it without your jaw dropping in awe. From the first iPhone to generative AI and everything in between, major breakthroughs across computing, networks, biotech, and energy have not only changed how the world works, but how we see it. Let's take a deeper look at 20 ways technology has advanced in the last 20 years.
 Matthew Yohe (talk) on Wikimedia
Matthew Yohe (talk) on Wikimedia
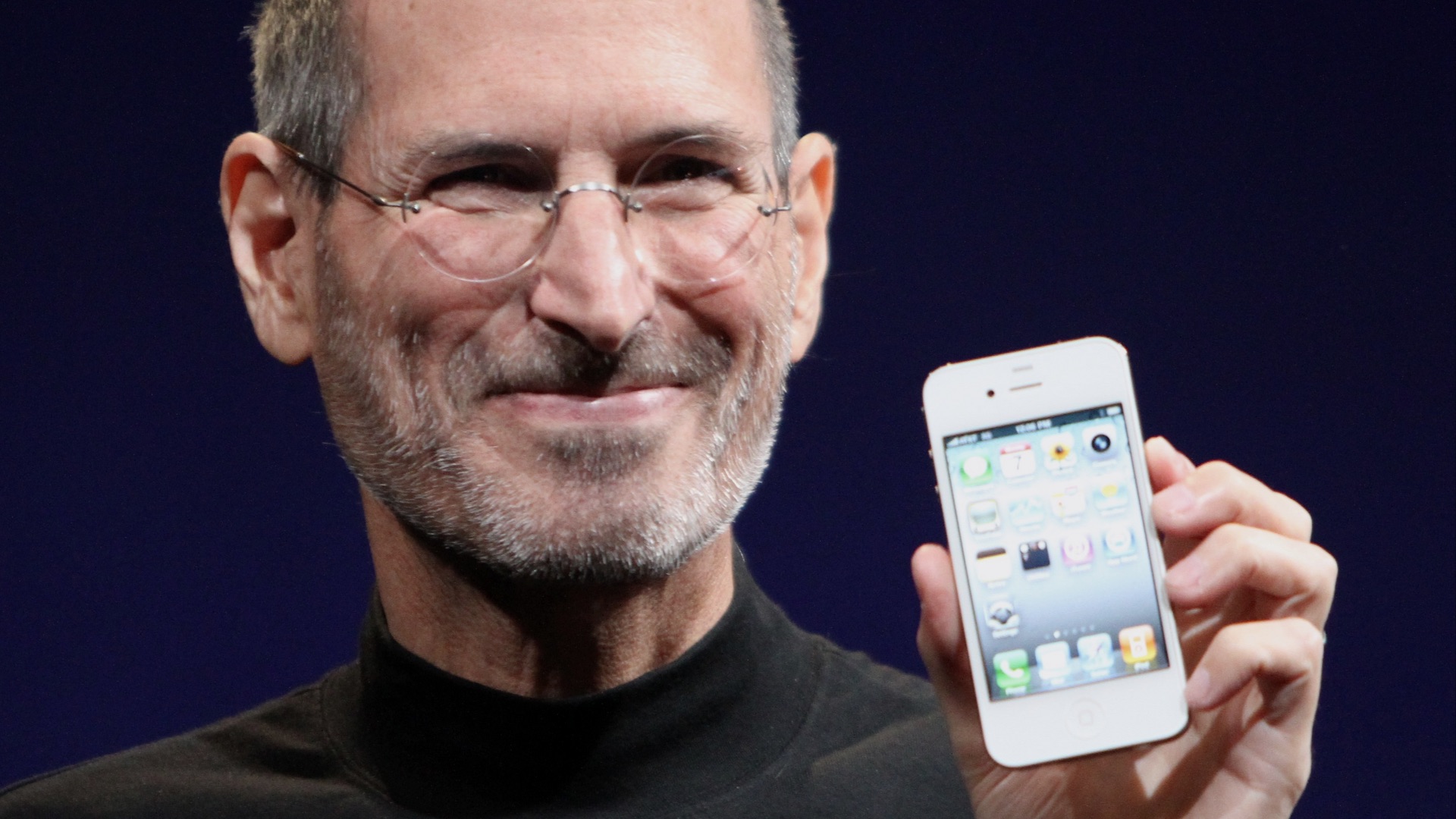
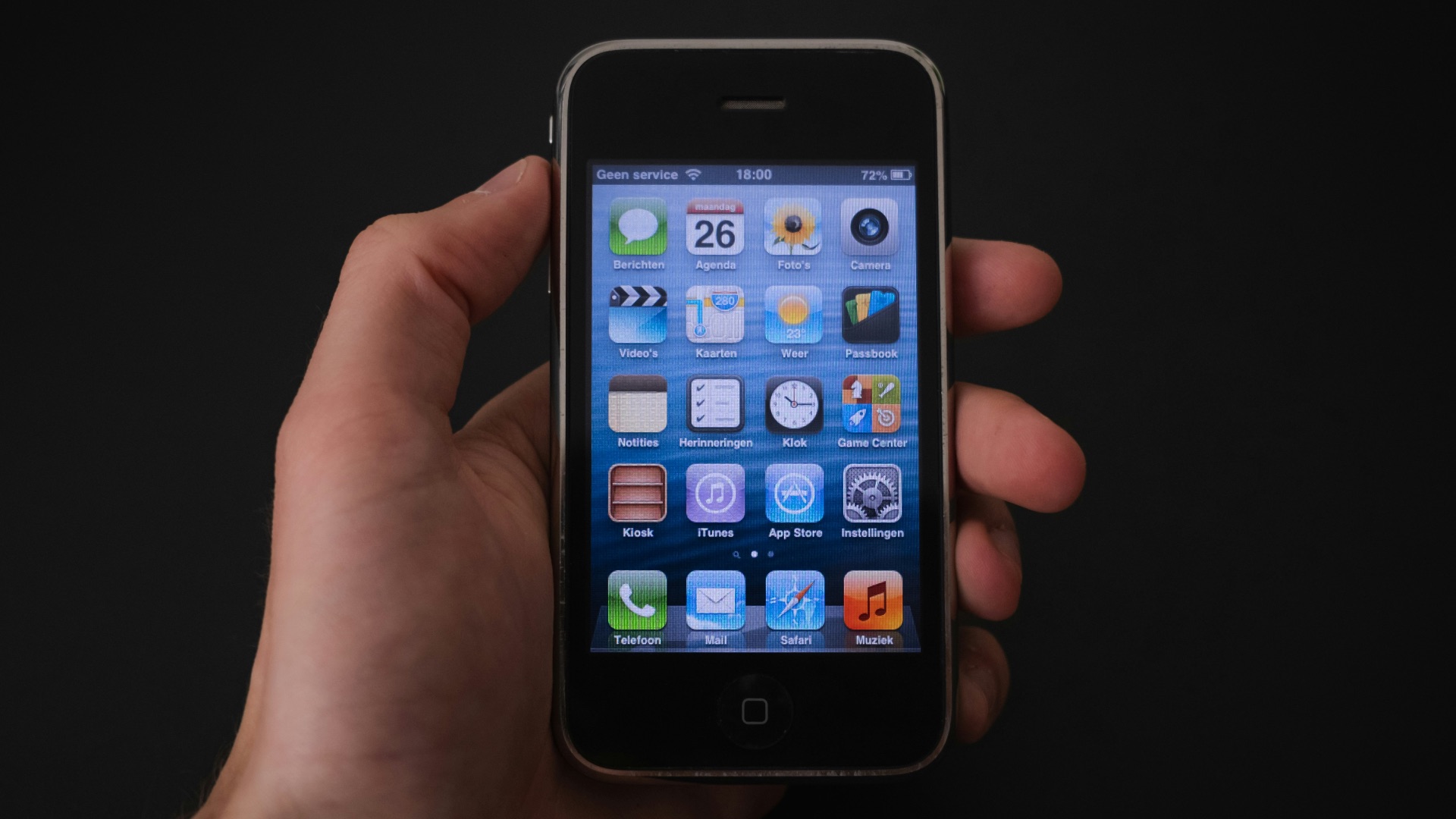
1. Your Phone Turned Into a Pocket Computer
Phones used to be mainly for calls and texts, but now they handle photos, maps, payments, and work in one place. What prompted this jump? The key milestone was the 2007 iPhone announcement, where then co-founder of Apple Steve Jobs framed the device as an all-in-one touchscreen product: a phone, an iPod, and an internet communicator. That approach helped shape what most modern smartphones became.
 Jonas Vandermeiren on Unsplash
Jonas Vandermeiren on Unsplash
2. Mobile Internet Stopped Feeling Like a Constant Struggle
With 4G LTE, this major network upgrade made mobile browsing and streaming much more dependable than older mobile systems. It’s part of why loading maps, watching videos, or sending large files on your phone became normal instead of tasks that tested your patience. In short, LTE helped make “on the go” internet actually usable.
3. 5G Helped Boost Networks Even More
If you thought 4G LTE was fast, think again. 5G is the newer mobile network generation designed to handle more connected devices and respond faster, especially in busy areas. That matters because you’re not just sharing the network with other phones anymore, but also with hotspots, wearables, cars, and all kinds of connected gear. The goal isn't just speed, but smoother performance under pressure.
4. “The Cloud” Made Computing Feel Like a Utility
It might sound a little technical, but let's break it down: cloud computing essentially means companies can rent computing power and storage on demand instead of buying racks of servers up front. This changed how quickly apps and websites can grow, because capacity can expand without waiting on new physical hardware deliveries.
5. Software Updates Got Easier to Ship Without Surprises
If you work in tech, you might already know what software containers are, but for those who don't, here's a simplified explanation. A "container" is basically a neat package that includes an app plus what it needs to run consistently, which helps teams avoid the classic problem where something works in one place and breaks in another because the setup is slightly different. As a result, many products can update more frequently with fewer disruptions, allowing for more efficient work.
6. Big Online Services Became More Stable Behind the Scenes
Websites and apps are often made of many small parts, and if one part fails, you don’t want the whole service to go down with it. Tools like Kubernetes, an open-source platform originally designed by Google, help keep services running by automatically restarting broken parts and spreading work around when traffic jumps.
 Raysonho @ Open Grid Scheduler / Grid Engine on Wikimedia
Raysonho @ Open Grid Scheduler / Grid Engine on Wikimedia
7. Computer Storage Got Dramatically Faster in Real Use
If your computer feels snappy to you, you can thank the storage for not dragging everything else down. Newer SSD standards in particular have helped computers read and write data faster, which improves startup times and how quickly large files move. That’s part of why many laptops and desktops now boot quickly and handle large files without feeling sluggish. In everyday terms, your computer spends less time “waiting on the drive.”
8. Wi-Fi Got Better at Handling Lots of Devices at Once
You might just think of Wi-Fi as the thing that gets you connected to the internet, but there are a lot of updates and things going on behind the scenes to give you the speed and performance you expect. Wi-Fi 6, for example, focused on making busy networks work better, especially when many devices are connected and competing for bandwidth. Wi-Fi 7, on the other hand, continues that push with improvements aimed at higher performance and smoother sharing in demanding settings.
 Praveen kumar Mathivanan on Unsplash
Praveen kumar Mathivanan on Unsplash
9. Streaming Became the Default Way to Watch Video
Years ago, you might have been bummed if you missed a scheduled broadcast, since there would be no convenient way to rewatch an aired episode. But now? Streaming platforms have changed how people watch almost everything; Netflix’s introduction of streaming in 2007 is an early milestone in that shift toward on-demand viewing. Want to start a new series or watch reruns? All you have to do is press play.
10. Video Calls Became Much More Standard & Accessible
Voice calls were the default for many years before revolutionary platforms like Skype emerged. Nowadays, for anything from school to work, you can easily hop on a video call wherever, whenever, to connect with whoever you need.
11. Computers Got Far Better at Recognizing Images
Photo apps and services can now recognize faces, objects, and scenes far more accurately than they used to, so if you've noticed the difference, you're right on the nose. This improvement accelerated in the 2010s when deep-learning systems started outperforming older methods on major image-recognition tests.
12. The Boom of AI
When OpenAI released ChatGPT in 2022, the whole landscape changed. Now, if you had a specific question, need help with deep research, or want to generate content or code, generative AI is there to assist you. Advancements in AI have been rapid as well, and things will likely only get more powerful from here on out.
13. The Web Became More Private by Default
You might not notice it when you're visiting webpages, but links with HTTPS are much more secure than those starting with HTTP, as it encrypts the connection between your device and a website. What does this mean for you? You can browse much more safely and privately than before.
 Glenn Carstens-Peters on Unsplash
Glenn Carstens-Peters on Unsplash
14. Beyond Passwords
Nowadays, you don't have to memorize a long, complicated password if you don't want to. WebAuthn is a standard that supports stronger sign-ins using cryptographic credentials instead of reusable passwords, and passkeys build on that idea so you can sign in using your device’s built-in security, often with a fingerprint or face scan. The goal is simpler sign-ins with fewer headaches (and scams).
 Volodymyr Kondriianenko on Unsplash
Volodymyr Kondriianenko on Unsplash
15. Private Messaging Got Better
Modern end-to-end encrypted messaging aims to protect your messages even if a key is compromised later. The “Double Ratchet” design, for example, is a well-known method that keeps updating encryption keys as a conversation continues, which helps reduce what an attacker could learn. This means you can rest assured when chatting with your loved ones.
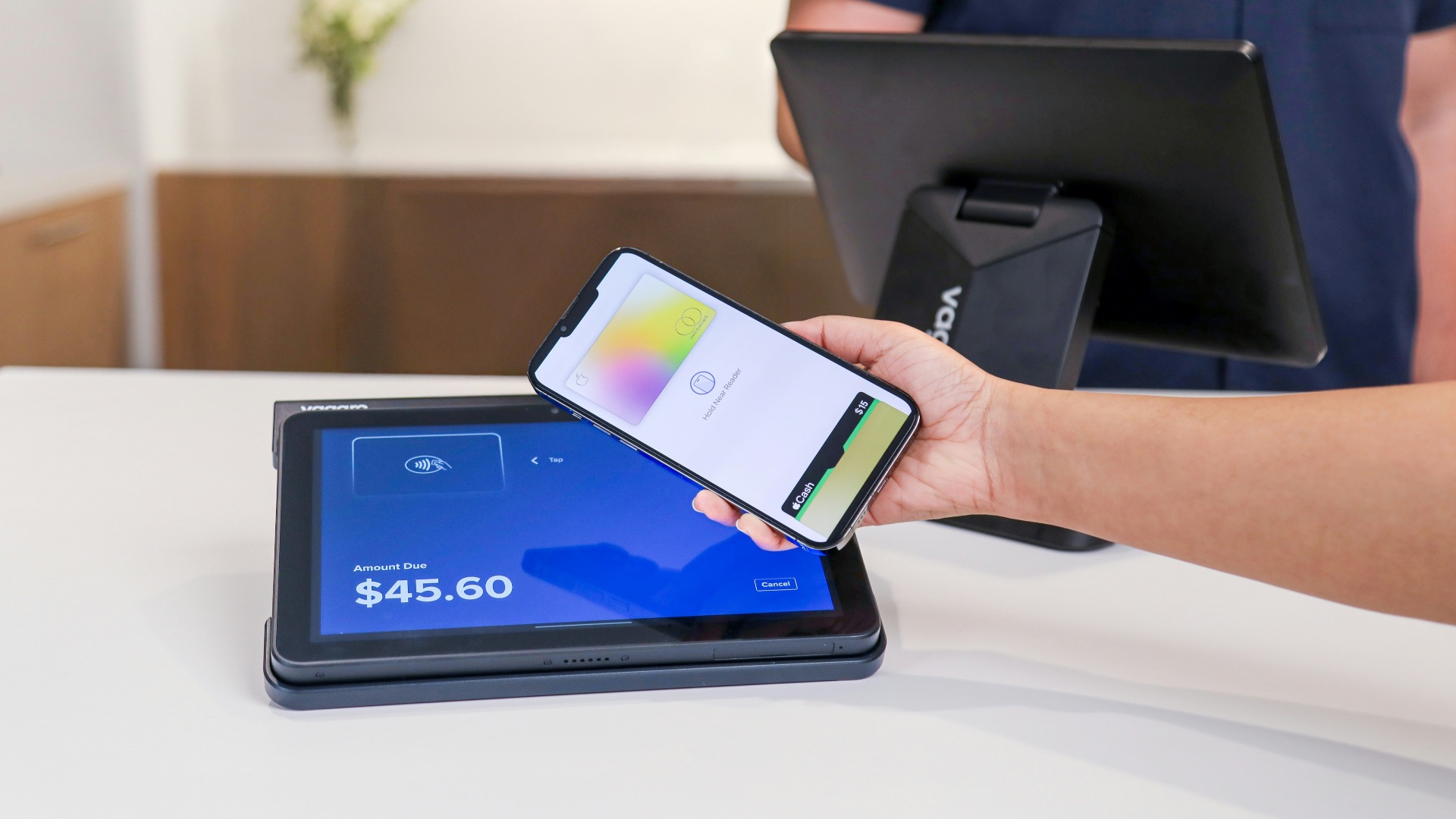
16. Paying with a Phone Became Normal & More Secure
Back in the day, you likely carried cash and physical cards with you all the time. Now? Technology like Apple Pay and Google Pay means you can take advantage of contactless technology and security features designed to reduce exposure of your actual card details. What you feel is speed and convenience, while the system aims to reduce common payment risks.
17. Reading DNA Became Far Cheaper & More Routine
Advancements in tech have benefited scientists, too. DNA sequencing is the process of reading genetic information, and its cost has dropped significantly over time. This cost decline has helped expand medical research and large genetics studies, which is a big win.
18. Gene Editing Became More Direct With CRISPR
CRISPR-Cas9 is a gene-editing tool that acts like a programmable way to cut DNA at a chosen spot, so changes can be made more precisely than many older methods. This has made genetic research faster to test and iterate, and editing genes has become more practical, not merely theoretical.
19. mRNA Vaccines Showed a Faster Way to Build Certain Vaccines
None of us wants to be reminded of the pandemic, but there is a silver lining: mRNA vaccines showed that once scientists know what they’re targeting, a vaccine can often be designed much faster than older approaches. They work by giving your cells instructions to make a harmless viral protein (or piece of one), so your immune system learns to recognize it. That doesn’t guarantee an instant rollout, but it could make it easier to develop updated vaccines faster during future outbreaks.
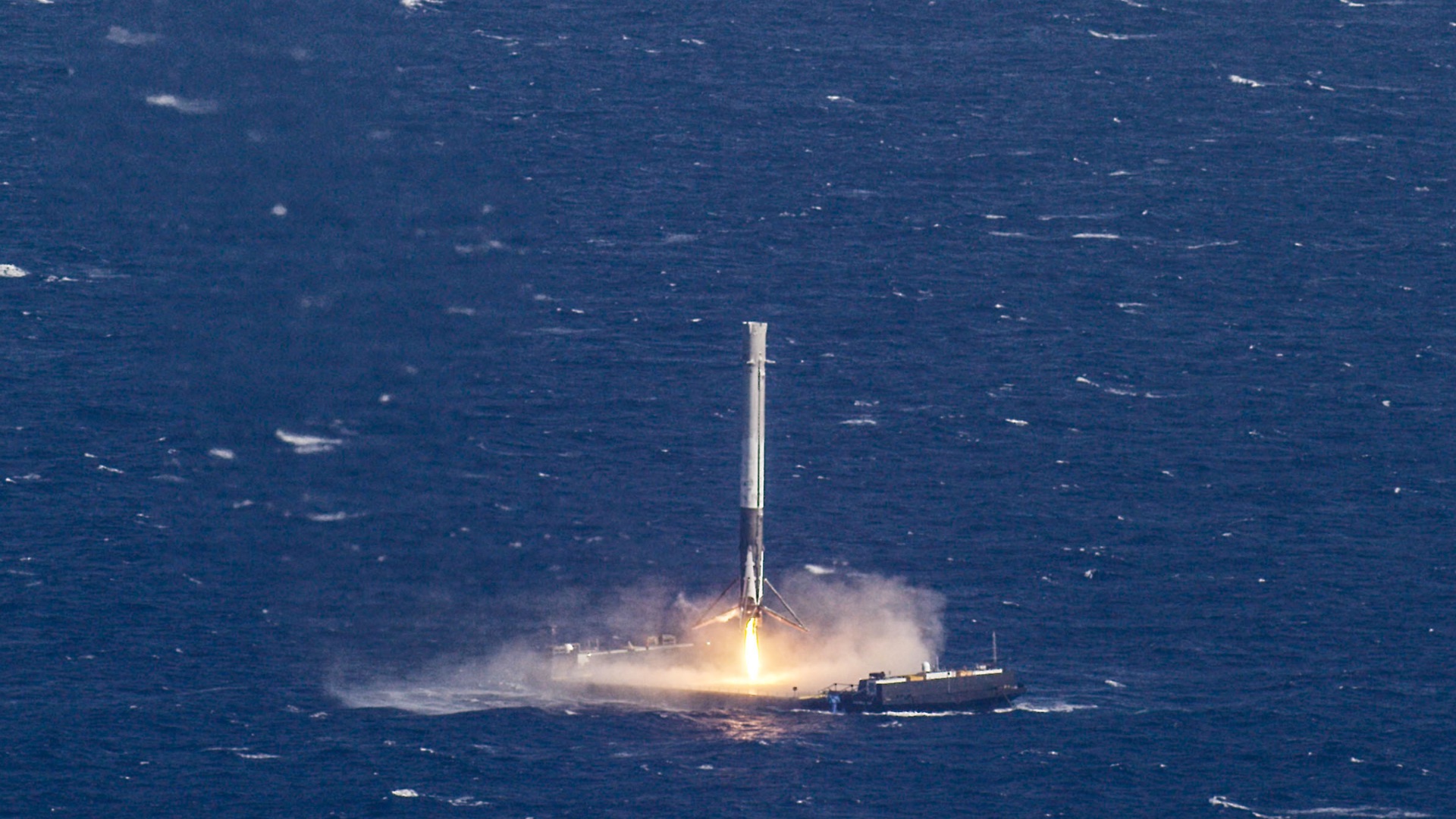
20. Reusable Rockets Changed What Space Launches Can Look Like
Space fans, this one's for you. For a long time, most rockets were discarded after launch, which kept costs stubbornly high. But in December 2015, SpaceX successfully landed an orbital-class Falcon 9 first stage after a mission, helping demonstrate that reuse could work in real operations. That success helped push the broader industry toward taking reusability seriously.